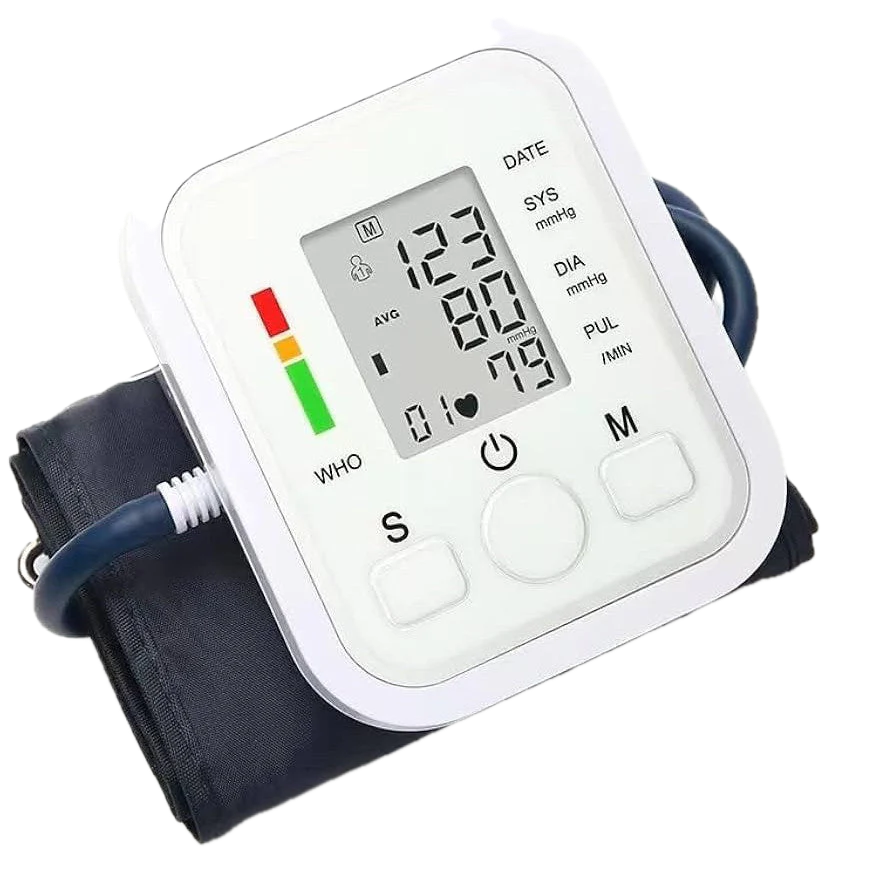
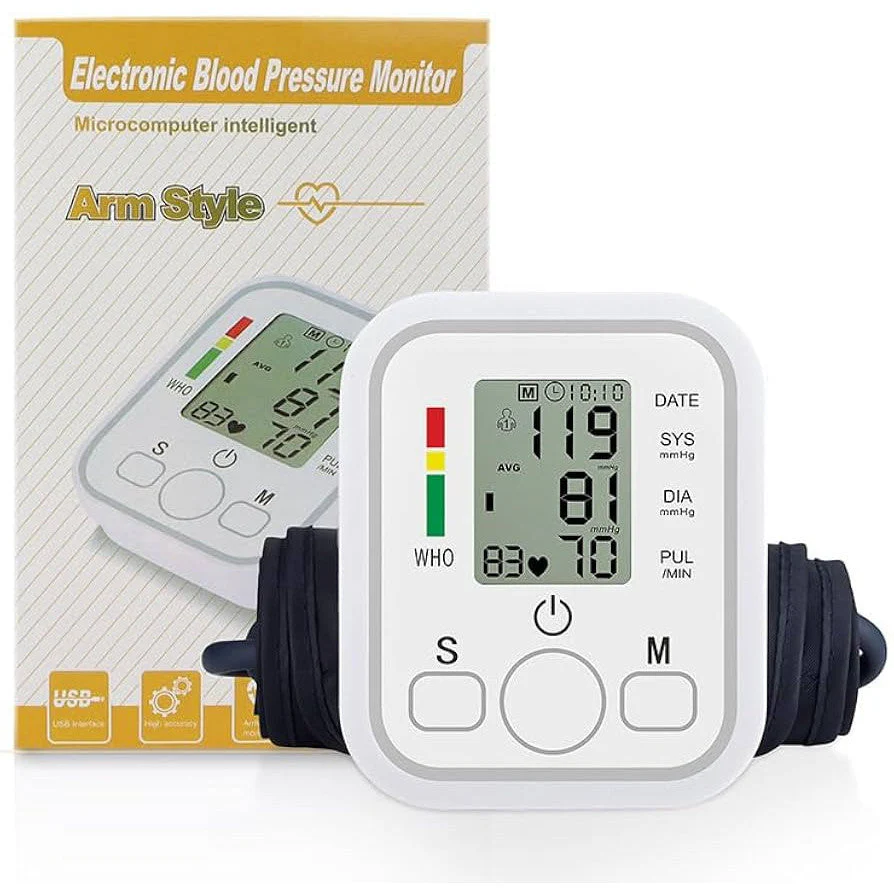
Blood Pressure Monitor Upper Arm
Blood pressure monitors are primarily used to measure blood pressure, which is the force of blood pushing against the walls of your arteries. They are essential for diagnosing and managing conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure) and hypotension (low blood pressure). Home monitoring is also valuable for tracking the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medication.
Here’s a more detailed breakdown of their uses:
1. Diagnosis:
-
High Blood Pressure (Hypertension):Blood pressure monitors are crucial for identifying and diagnosing hypertension, a condition that significantly increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
-
Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension):While less common, blood pressure monitors can also help diagnose hypotension, which can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting.
-
“White Coat Hypertension”:These devices can help determine if blood pressure spikes are solely due to anxiety in a clinical setting, as opposed to true hypertension.
-
Masked Hypertension:Conversely, they can also detect masked hypertension, where blood pressure appears normal in a doctor’s office but is elevated at home.
2. Monitoring and Management:
-
Tracking Treatment Effectiveness:Home blood pressure monitoring allows individuals and their healthcare providers to assess whether lifestyle changes (diet, exercise) or medications are effectively controlling blood pressure.
-
Adjusting Treatment Plans:Regular monitoring helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions about adjusting medication dosages or other aspects of treatment.
-
Promoting Self-Care:Monitoring blood pressure at home can empower individuals to take a more active role in managing their health and potentially improve their motivation to make positive lifestyle changes.
-
Reducing Healthcare Costs:Early detection and management through home monitoring may lead to fewer doctor visits and potentially lower overall healthcare costs.
3. Types of Blood Pressure Monitors:
- Digital Monitors: These are the most common type for home use, offering ease of use and automatic readings.
- Aneroid Sphygmomanometers: These are manual devices that require a stethoscope for taking readings.
- Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors: These devices record blood pressure over a 24-hour period, providing a comprehensive picture of blood pressure fluctuations.